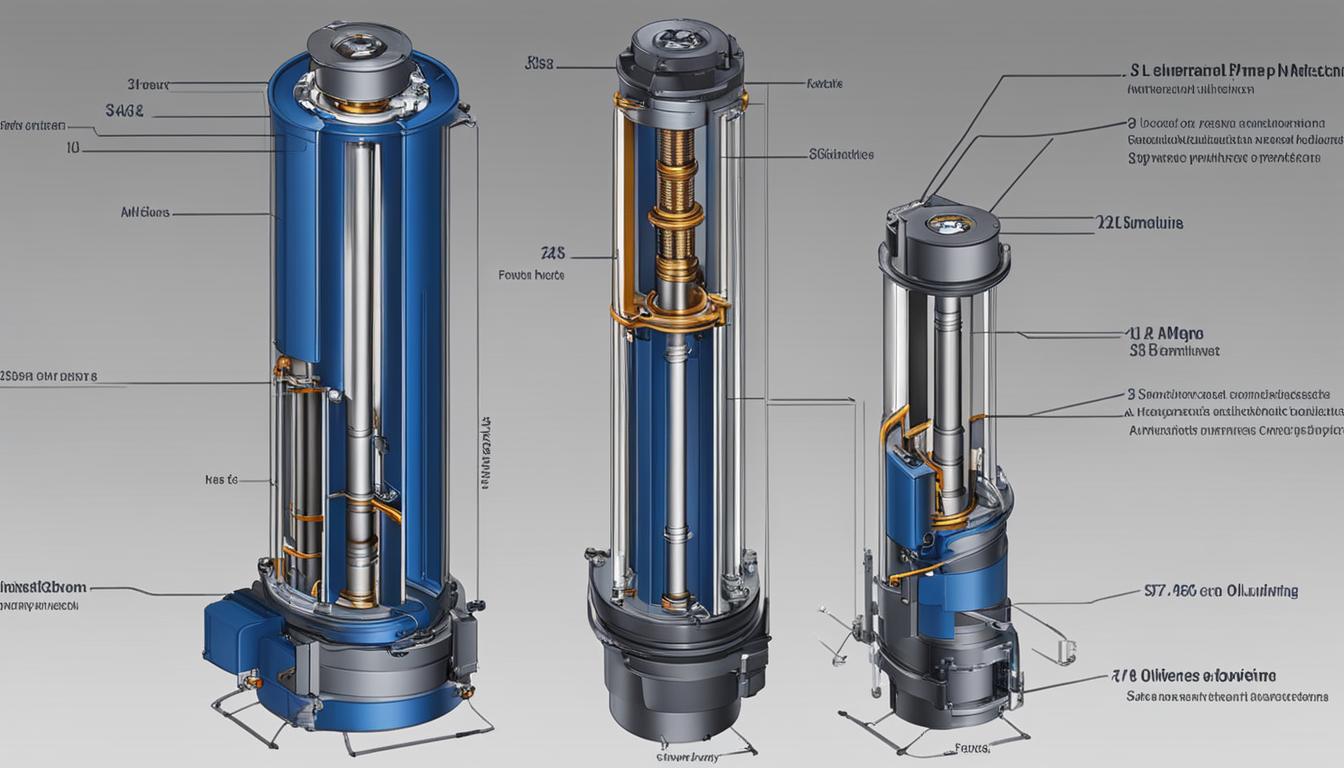
When it comes to submersible pumps, proper oil selection plays a crucial role in their performance and longevity. Whether you are looking for the best oil for your submersible pump or seeking guidance on oil specifications and maintenance, understanding the different types of oil used in these pumps is essential.
Submersible pumps consist of various components such as the head assembly, motor and turbine pump, waterproof electric wire, and discharge pipe. Of particular importance is the motor, which can be oil-lubricated or water-lubricated. Oil-lubricated motors are sealed to prevent water entry, and the oil used in these motors serves as a lubricant for the bearings, windings, and rotor.
There are different types of oil that can be used in oil-lubricated motors, including mineral oil or synthetic base oil. These oils come in varying viscosity grades and additive systems, providing options for different operating conditions and performance requirements.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper oil selection is crucial for the performance and longevity of submersible pumps
- Submersible pumps can have oil-lubricated or water-lubricated motors
- Oil-lubricated motors use oil as a lubricant for the bearings, windings, and rotor
- Different types of oil, such as mineral or synthetic base oil, can be used
- Oil selection depends on factors like viscosity grade and additive systems
Components of a Submersible Pump
When it comes to submersible pumps, understanding the different components is essential in grasping how these devices function. A submersible pump consists of several key elements that work together to facilitate the pumping action.
Head Assembly
The head assembly is a crucial component that includes the main switch and starter. It serves as the control center of the pump, allowing for easy operation and monitoring.
Motor and Turbine Pump
The motor is another vital part of a submersible pump. It can be either oil-lubricated or water-lubricated, depending on the specific design. The motor generates the power necessary for the pump’s operation. Alongside the motor, there is a turbine pump, responsible for drawing and moving water.
Waterproof Electric Wire
A submersible pump requires a waterproof electric wire to supply power to the motor. This wire is specially designed to withstand submersion and ensure safe and reliable electrical connections.
Discharge Pipe
The discharge pipe is responsible for ejecting the pumped water from the submersible pump. It provides a pathway for the water to flow and directs it to its intended destination.
By understanding the components of a submersible pump, you can gain insight into how these devices operate and make informed decisions when it comes to installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Head Assembly | The control center of the pump includes the main switch and starter |
| Motor and Turbine Pump | Generates power and moves water respectively to facilitate pumping action |
| Waterproof Electric Wire | Safely supplies power to the motor under submersion |
| Discharge Pipe | Ejects pumped water from the submersible pump |
Types of Oil for Submersible Pumps
When it comes to submersible pumps, there are two main types of motors: oil-lubricated motors and water-lubricated motors. Oil-lubricated motors are designed with proper sealing to prevent water entry, relying on oil as a lubricant for critical components such as bearings, windings, and rotors. The type of oil used in these motors plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the submersible pump.
Different types of oil can be used for submersible pumps, with options such as mineral oil or synthetic base oil. Mineral oil is a commonly used traditional lubricant, while synthetic base oil is known for its higher performance and resistance to extreme conditions. The choice between these oils depends on factors such as the specific application requirements, environmental considerations, and cost constraints.
Viscosity grade and additive systems are two important factors to consider when selecting the oil for a submersible pump. Viscosity grade refers to the oil’s resistance to flow and its ability to provide lubrication at different temperatures. The appropriate viscosity grade ensures optimal lubrication under normal operating conditions, preventing excessive wear and tear on the motor components.
Another essential consideration is the additive system used in the oil. Additives are substances added to lubricating oils to enhance their performance and provide additional protection against corrosion, oxidation, and wear. The right combination of additives can improve the oil’s stability, thermal resistance, and resistance to contaminants, ensuring the submersible pump operates efficiently and reliably.
To summarize, selecting the right type of oil for submersible pumps is crucial for their performance and longevity. Whether it’s mineral oil or synthetic base oil, each option offers distinct advantages and considerations. The viscosity grade and additive system should also align with the specific requirements of the application to ensure optimal pump operation.

| Oil Type | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Mineral Oil | – Widely available and cost-effective – Suitable for standard operating conditions |
– May have limited performance in extreme temperatures – Requires regular monitoring and maintenance |
| Synthetic Base Oil | – High-performance lubrication in extreme conditions – Enhanced thermal stability and resistance to oxidation |
– Higher cost compared to mineral oil – Specific compatibility considerations for certain materials |
Benefits and Drawbacks of Oil-Filled Submersible Pumps
Oil-filled submersible pumps offer a range of benefits that make them popular in various applications. First and foremost, these pumps have a longer lifespan compared to other types of pumps. This is mainly due to the oil that lubricates the bearings, resulting in reduced friction and wear. The oil also provides efficient cooling for the motor, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance.
Another advantage of oil-filled submersible pumps is their higher efficiency at greater depths. These pumps can operate effectively even in deep wells, delivering consistent water flow with minimal energy consumption. Additionally, they exhibit improved resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for harsh environments where other pumps may fail.
Oil-filled submersible pumps are known for their power and performance in extreme temperatures. They can withstand both freezing cold and scorching heat, making them reliable options for applications in extreme climates.
“Oil-filled submersible pumps have a longer lifespan, efficient cooling, higher efficiency at greater depths, improved resistance to corrosion, more power, and better performance in extreme temperatures.”
However, it’s essential to consider the drawbacks of oil-filled submersible pumps as well. One potential concern is the risk of oil leakage over time. Despite being properly sealed, there is always a possibility of oil seeping out, which can lead to environmental contamination.
Another drawback is the increased weight of oil-filled submersible pumps. This can make them challenging to handle and install, especially in situations where portability is important.
Maintenance requirements are also higher for oil-filled pumps. Regular oil changes are necessary to keep the pump running smoothly and prevent any damage caused by degraded oil. Contamination of the oil can also lead to reduced efficiency, as dirt and contaminants can cause clogs and hinder the performance of the pump.
Additionally, oil-filled submersible pumps may not be suitable for applications that require a clean environment. The oil used in these pumps tends to attract dirt and contaminants, which can affect the water quality in certain settings.
Oil-filled submersible pumps are also limited in their temperature range. They may not perform well in extremely high or low temperatures, which can restrict their usage in certain industries or climates.
Lastly, oil-filled submersible pumps generally come at a higher cost compared to other options. The initial investment as well as the ongoing maintenance expenses are factors that need to be considered when choosing the right pump for a specific application.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
Water-filled submersible pumps offer numerous benefits compared to other types of pumps. Their energy efficiency allows for lower energy consumption and cost savings in the long run. These pumps are built to withstand corrosion and other forms of wear and tear, ensuring durability and a longer lifespan. Additionally, water-filled submersible pumps have low maintenance requirements, reducing the time and effort needed for upkeep.
One of the standout features of water-filled submersible pumps is their quiet operation. This makes them ideal for residential areas or applications where noise levels need to be minimized. Furthermore, their versatility allows them to be used in a wide range of settings, from small residential wells to industrial operations.
Another advantage of water-filled submersible pumps is their ease of installation. These pumps can be installed without the need for professional assistance, saving both time and money. Once installed, water-filled submersible pumps deliver reliable operation, ensuring consistent performance and peace of mind.
However, there are a few drawbacks associated with water-filled submersible pumps. Size limitations can be a concern for larger applications that require higher pumping capacities. Additionally, water-induced corrosion may lead to increased maintenance requirements, although these pumps generally have lower maintenance needs compared to other types.
Another factor to consider is the cost. Water-filled submersible pumps may have a higher initial cost compared to alternative pump types. However, the energy efficiency and durability of these pumps can offset the higher upfront investment over time.
Installation complexity is another drawback to be aware of when considering water-filled submersible pumps. While they offer easy installation, there may still be certain complexities involved, depending on the specific application requirements.
Water-filled submersible pumps also have a dependence on water level for proper functioning. These pumps require a certain water level to operate efficiently, so fluctuations in water level may impact their performance.
Furthermore, the risk of contamination is a consideration when using water-filled submersible pumps. They may be vulnerable to contamination from pollutants in the water, which could affect the pump’s performance and lifespan.
Lastly, water-filled submersible pumps may have limited use in environments where the water contains high amounts of sediment or debris. These pumps are generally more suitable for pumping clean or relatively clean water.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
Here’s a summary of the benefits and drawbacks of water-filled submersible pumps:
| Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
| Energy efficiency | Size limitations |
| Durability | Maintenance requirements due to water-induced corrosion |
| Low maintenance | Higher cost compared to other types of pumps |
| Quiet operation | More complex installation process |
| Versatility | Dependence on water level |
| Easy installation | Risk of contamination from pollutants |
| Reliable operation | Limited use in dirty water |
Despite these drawbacks, water-filled submersible pumps remain a popular choice for many applications due to their overall advantages and reliable performance.

Factors to Consider in Pump Selection
When selecting a submersible pump, it is important to take various factors into consideration. These factors will help you determine the most suitable pump for your specific needs and ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Application-specific requirements: Start by evaluating the specific requirements of your application. Consider factors such as the pumping depth, flow rate, pressure, and the type of liquid being pumped. These details will help you determine the pump’s capacity and capabilities.
Environmental considerations: Assess the surrounding environment in which the pump will operate. For oil-filled pumps, it is crucial to consider the risk of oil leakage and potential environmental damage. Water-filled pumps, on the other hand, may be prone to water contamination if used in areas with high levels of sediment or debris.
Cost considerations: Take into account both the initial cost of the pump and the long-term maintenance and operational expenses. Oil-filled pumps may require regular oil changes, adding to the maintenance costs, while water-filled pumps may need additional measures for corrosion prevention.
Maintenance requirements: Understand the maintenance requirements of the pump. Oil-filled pumps generally demand regular oil changes and may have additional maintenance needs due to the lubricant. Water-filled pumps may require measures to prevent corrosion and ensure the longevity of the pump.
Performance expectations: Define your performance expectations in terms of flow rate, pressure, and efficiency. Ensure that the selected pump can meet these requirements effectively. Consult the pump’s specifications or seek expert advice to determine its performance capabilities.
Comparison of Factors for Pump Selection
| Factors | Oil-Filled Pumps | Water-Filled Pumps |
|---|---|---|
| Application-specific requirements | Consider the pumping depth, flow rate, pressure, and the liquid being pumped. | Assess the specific requirements of your application. |
| Environmental considerations | Oil leakage risk and potential environmental damage. | Water contamination risk in high sediment or debris areas. |
| Cost considerations | Initial cost, regular oil changes, and maintenance expenses. | Initial cost and corrosion prevention measures. |
| Maintenance requirements | Regular oil changes and additional maintenance due to the lubricant. | Corrosion prevention measures and maintenance to ensure longevity. |
| Performance expectations | Efficiency, flow rate, and pressure as specified by the pump. | Ensure the pump can meet the desired flow rate, pressure, and efficiency requirements. |
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision when selecting a submersible pump. This will not only ensure that the pump meets your application’s specific requirements but also optimize its performance and efficiency.

Application Examples for Oil-Filled Submersible Pumps
Oil-filled submersible pumps are highly versatile and find extensive application in various industries that demand durability, longevity, and reliable performance, even in extreme temperatures. Let’s explore some notable examples:
Mining Industry
In the mining industry, oil-filled submersible pumps are indispensable for dewatering operations, ensuring efficient removal of water from underground mines. These pumps are designed to withstand harsh conditions and constant exposure to abrasive materials. The durability and longevity of oil-filled submersible pumps make them ideal for extended periods of continuous pumping, providing optimal performance in challenging mining environments.
Construction Industry
The construction industry heavily relies on oil-filled submersible pumps to handle various tasks, such as draining pits, excavations, and construction sites. These pumps offer durability and longevity, making them capable of withstanding prolonged use in demanding construction projects. Oil-filled submersible pumps excel at handling high-power output requirements, providing reliable performance to keep construction sites dry and operational.
Extreme Temperatures
Oil-filled submersible pumps are specially designed to operate in extreme temperature conditions, making them suitable for challenging environments such as oil refineries, chemical plants, and industrial settings with high-temperature operations. These pumps maintain their efficiency and performance levels in extreme heat, ensuring smooth operations even when exposed to elevated temperatures. With their ability to withstand extreme temperature fluctuations, oil-filled submersible pumps are a reliable choice for critical applications where temperature control is crucial.

Application Examples for Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
Water-filled submersible pumps have a wide range of applications, making them a versatile choice for various water-related needs. Let’s explore some typical examples of how these pumps are utilized:
- Residential Wells: Water-filled submersible pumps are commonly used to extract water from residential wells. With their efficient operation and low maintenance requirements, these pumps provide a reliable supply of water for households.
- Agricultural Irrigation: In the agricultural sector, water-filled submersible pumps play a crucial role in irrigation systems. Their energy efficiency enables cost-effective watering of crops, while their reliability ensures consistent water delivery for optimal plant growth.
- Lake Water Extraction: Water-filled submersible pumps are ideal for extracting water from lakes or other bodies of water. Whether for industrial or commercial purposes, these pumps offer a quiet operation and a low maintenance profile, making them a convenient choice.
With their energy-efficient performance and capability to deliver water effectively, water-filled submersible pumps are widely preferred in applications that prioritize sustainability and cost-effectiveness. Their versatility extends beyond residential and agricultural use, finding relevance in industrial settings as well.
Industrial Applications:
In industries requiring large-scale water extraction, water-filled submersible pumps are employed to meet high-volume demands. Their reliable operation and low maintenance requirements make them suitable for industrial and commercial applications that depend on a continuous water supply.
“Water-filled submersible pumps are efficient and reliable, making them the go-to choice for residential wells, agricultural irrigation, and lake water extraction. These pumps deliver water effectively, ensuring a steady supply for various applications.”
Conclusion
After considering the various factors, it is evident that choosing between oil-filled and water-filled submersible pumps requires careful thought and evaluation. The specific requirements of the application, environmental considerations, cost factors, maintenance requirements, and performance expectations all play a crucial role in making the optimal pump selection.
Oil-filled submersible pumps offer significant advantages such as longer lifespan, efficient cooling, higher efficiency at greater depths, and improved resistance to corrosion. However, they also come with drawbacks, including the potential for oil leakage and increased maintenance requirements. On the other hand, water-filled submersible pumps are energy-efficient, durable, low-maintenance, and versatile. Yet, they do have limitations, such as size restrictions and maintenance needs due to water-induced corrosion.
It is vital to carefully assess these factors and their relevance to your specific needs and environment before making a decision. By doing so, you can ensure that you choose the optimal pump type that aligns with your requirements, offers reliable performance, and provides long-term value. Whether it be oil-filled or water-filled submersible pumps, making an informed decision ensures the efficient operation of your submersible pump and the success of your application.
FAQ
What are the components of a submersible pump?
The components of a submersible pump include a head assembly, motor and turbine pump, waterproof electric wire, and a discharge pipe.
What types of oil are used in submersible pumps?
Submersible pumps can use various types of oil, such as mineral oil or synthetic base oil, with different viscosity grades and additive systems.
What are the benefits and drawbacks of oil-filled submersible pumps?
Oil-filled submersible pumps offer benefits like longer lifespan, efficient cooling, higher efficiency at greater depths, improved resistance to corrosion, more power, and better performance in extreme temperatures. However, they also have drawbacks such as the potential for oil leakage, increased weight, increased maintenance requirements, reduced efficiency due to contamination, reduced suitability for clean applications, limited temperature range, and higher cost compared to water-filled submersible pumps.
What are the benefits and drawbacks of water-filled submersible pumps?
Water-filled submersible pumps offer benefits like energy efficiency, durability, low maintenance requirements, quiet operation, versatility, easy installation, and reliable operation. However, they also have limitations such as size restrictions, maintenance requirements due to water-induced corrosion, higher cost, more complex installation, dependence on water level, risk of contamination, and limited use in dirty water.
What factors should be considered in pump selection?
Factors to consider in pump selection include application-specific requirements, environmental considerations, cost considerations, maintenance requirements, and performance expectations.
Can you provide examples of applications for oil-filled submersible pumps?
Oil-filled submersible pumps are commonly used in industries such as mining and construction, where durability, longevity, and resistance to extreme temperatures are important.
What are some examples of applications for water-filled submersible pumps?
Water-filled submersible pumps find applications in residential wells, agricultural irrigation, and extracting water from lakes or other bodies of water. They are known for their energy efficiency and versatility.